|
Cadillac
|
1902
- |
Country: |
 |
|
CADILLAC WAS the branch of the early General Motors that led the way in the engineering and manufacturing fields, just as
Buick led in production. Long before World War 1, the Cadillac was well established as one of the finest cars built in America and, as the recipient of two Dewar Trophies, it had gained world-wide fame.
Few cars have remained as true to their original purposes and traditions as has the Cadillac. The Cadiliac car can, in fact, be said to have added lustre to the name it was given. While a commissioned officer in the Royal French Army, Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac founded the city of Detroit, as a fur trading centre, in 1701.
Cadillac was later honoured in several ways by his King, Louis XIV, which served to obscure his rather doubtful family origins in the small town in Gascony where he was born. The Cadillac family did have a coat of arms, however, dating from the 11th century, and it was adopted for the Cadillac car. It remains the only coat of arms, of authentic origin, in use on any American car today.
Cadiliac, of course, arrived in Detroit two hundred years too early to start an automobile company. His name was chosen for the company and the automobile, in 1902, by a well-to-do lumber merchant, William H. Murphy. Several years earlier, Murphy had backed a young mechanic,
Henry Ford, in the founding of a new firm to produce cars to Ford's designs.
Ford had differences with his backers, however, and left the company to go his own way. Murphy and his associates were planning to give up their car-building venture after this, but decided to consult with the company that was to make engines for their cars, the Leland and Faulconer Manufacturing Company of Detroit.
The guiding spirit of Leland and Faulconer was Henry Martyn Leland, a skilled and highly-principled gunsmith and toolmaker. Born in Vermont in 1843, Leland was not a youngster at the turn of the century. Yet he had the vitality to suggest to Murphy that he push ahead with his car company, using a horizontal single-cylinder engine that had been designed at the Leland plant by Alanson P. Brush.
Craftsmanship A Creed; Accuracy A Law
Henry Leland entered the American motor industry almost by chance, rather than choice. It was to the young industry's great benefit that he did so, as Leland may have done more than any other individual to give this eager but untutored motor business a sense of responsibility toward fine engineering and high precision. From Leland's beliefs and practices came the Cadillac motto: 'Craftsmanship a creed; accuracy a law'. Leland wasn't present at the meeting on 22 August 1902 at which Murphy and his partners reorganised their motor car firm and named it the Cadiliac Automobile Company.
Two years later, when it was merged with Leland and Faulconer, it was again renamed the Cadiliac Motor Car Company. Henry Leland then became Cadillac's president. The first Cadillac car, the prototype of the Model A, was completed on 17 October 1902, and was shown in January 1903 at the New York Automobile Show. This first single-cylinder Cadillac was a primitive machine by the standards of the European cars of its day, but its simplicity, light weight and high ground clearance were just what America's atrocious roads required.
As Models A, B, E, F, K, M, S and T, 16,126 examples of the single-cylinder Cadillac were sold between 1903 and 1908. With various body styles, their prices ranged from $750 to $1,400. Detail improvements in the 1610cc engine increased its output from 7 to 10 horsepower during its lifetime. Fitted with a copper water jacket, the engine rested underneath the front seat and drove through a two-speed planetary transmission. The Model K, with a two-seater light runabout body, was the one that won Leland, Cadiliac, and Frederick Bennett, England's importer of Cadillacs, their respective places in the motor industry hall of fame.
They proved, with a dramatic demonstration at
Brooklands, in March 1908, that Cadillac cars were made from parts that were entirely interchangeable - a claim that few, if any, other car makers could boast at that time. It was taken for granted in those days that a certain amount of hand-fitting would always be necessary when replacing old and worn parts of a car with new ones. Prompted by Frederick Bennett, officials of Britain's Royal Automobile Club picked three new Cadillacs at random from the eight that were in stock in London at that time. They were driven to the Brooklands circuit, briefly tested to find out what their performance was, and then taken completely apart.
 A 1903 Cadillac 4 Seater 7hp, powered by a 1610cc engine.
A 1903 Cadillac 4 Seater 7hp, powered by a 1610cc engine.
 This is a 1904 Cadillac 9hp single cylinder 4 seater.
This is a 1904 Cadillac 9hp single cylinder 4 seater.
 1906 Cadillac 4 seater tourer.
1906 Cadillac 4 seater tourer.
 1906 4 seater Cadillac - one of the first 4 cylinder versions.
1906 4 seater Cadillac - one of the first 4 cylinder versions.
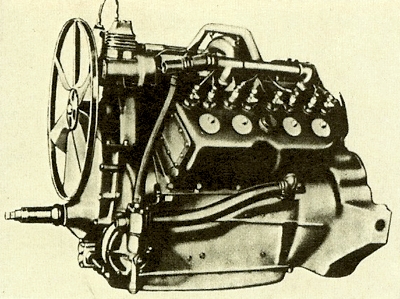 1914 Cadillac V8 engine, 5.1 liters and good for 70 bhp.
1914 Cadillac V8 engine, 5.1 liters and good for 70 bhp.
 1917 Cadillac 55 Landaulet Coupe.
1917 Cadillac 55 Landaulet Coupe.
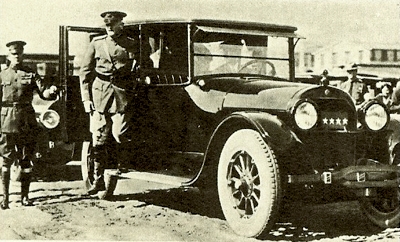 1918 Cadillac Model 57, with General Pershing stepping down.
1918 Cadillac Model 57, with General Pershing stepping down.
 1925 Cadillac V8 Suburban - a four door four seat tourer.
1925 Cadillac V8 Suburban - a four door four seat tourer.
 1931 Model 355 Cadillac - the model that introduced synchronised-shifting, or Synchro-Mesh.
1931 Model 355 Cadillac - the model that introduced synchronised-shifting, or Synchro-Mesh.
 One of the first Cadillacs fitted with the V16 was the 1931 sedan.
One of the first Cadillacs fitted with the V16 was the 1931 sedan.
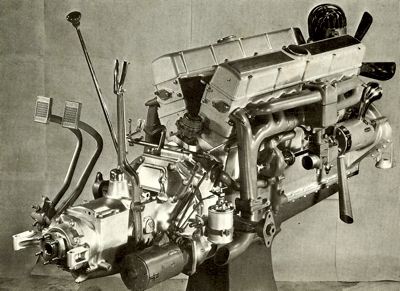 And here it is, the Cadillac V16, an overhead valve 7.4 liter producing 165 bhp at 3400 rpm. Designed by Ernest Seaholm, Cadillac's chief deisgner from 1923 to 1943.
And here it is, the Cadillac V16, an overhead valve 7.4 liter producing 165 bhp at 3400 rpm. Designed by Ernest Seaholm, Cadillac's chief deisgner from 1923 to 1943.
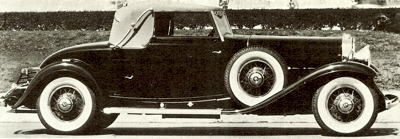 1931 Cadillac 452A, which was fitted with a V8.
1931 Cadillac 452A, which was fitted with a V8.
 1939 Cadillac V16 Fleetwood.
1939 Cadillac V16 Fleetwood.
 1939 Cadillac V16 Fleetwood, with hardtop rear and open air for Jeeves.
1939 Cadillac V16 Fleetwood, with hardtop rear and open air for Jeeves.
 1947 Cadillac Limousine, fitted with a V8 originally introduced in 1936 to replace the V12 and V16 engines. The cast iron V8 produced 150 bhp from 5.7 liters.
1947 Cadillac Limousine, fitted with a V8 originally introduced in 1936 to replace the V12 and V16 engines. The cast iron V8 produced 150 bhp from 5.7 liters.
 1947 Cadillac Limousine in profile.
1947 Cadillac Limousine in profile.
 1954 Cadillac Coupe de Ville, showing the start of the "Fins" era.
1954 Cadillac Coupe de Ville, showing the start of the "Fins" era.
 1958 Cadillac Sedan de Ville.
1958 Cadillac Sedan de Ville.
 1958 Cadillac Eldorado Brougham.
1958 Cadillac Eldorado Brougham.
 1959 Cadillac Fleetwood Sixty Special.
1959 Cadillac Fleetwood Sixty Special.
 1959 Cadillac Eldorado Hardtop.
1959 Cadillac Eldorado Hardtop.
 1964 Cadillac Eldorado Convertible.
1964 Cadillac Eldorado Convertible.
 1967 Cadillac Eldorado, the first Cadillac to feature front-wheel-drive. On the right is the more conventional 1967 Cadillac Fleetwood.
1967 Cadillac Eldorado, the first Cadillac to feature front-wheel-drive. On the right is the more conventional 1967 Cadillac Fleetwood.
 1967 Cadillac Eldorado.
1967 Cadillac Eldorado.
 1973 Cadillac Eldorado, fitted with a 8.2 liter V8 producing 400 bhp. Perfectly timed with the fuel crisis.
1973 Cadillac Eldorado, fitted with a 8.2 liter V8 producing 400 bhp. Perfectly timed with the fuel crisis. |
The RAC men then mixed up all the parts and threw in some new pieces taken from the spare parts supplies, for good measure. From these jumbled parts, two of Bennett's mechanics assembled three Model K Cadillacs again, the RAC representatives looking over their shoulders to make sure that they didn't hand-scrape the pieces to make them fit. Then all three of the completed Cadillacs ran 500 miles at Brooklands without the slightest trouble, and one of the three, picked again by the RAC, won its class in the 2000-mile Reliability Trial in June 1908.
It was hardly surprising that the RAC awarded Cadillac the coveted Dewar Trophy for that year, recognising the greatest advance made then by any motor car. Cadillac's growing reputation had attracted the attention of the legendary William Crapo Durant of. Flint, Michigan. Durant chose Cadiliac, along with Buick, Oldsmobile and Oakland, as a component of his General Motors Company in July 1909. Cadillac became a division of GM when the firm was reorganised as a corporation in 1916. This did not, however, mean that the high standards of Cadillac, set by Henry Leland and his son Wilfred, were lowered in any way by ace-salesman Durant.
The Most Moderately Priced Strictly High-Grade Motor Car In The World
Cadillac remained an independent operation, perhaps the most independent of all the GM divisions, building what it called 'the most moderately priced strictly high-grade motor car in the world'. Four-cylinder Cadillacs were produced, 67,167 of them in all, starting with the 5-liter Model D of 1905. A smaller four-cylinder car, the Model G, was launched in 1907 and continued until 1912. That was the year that Cadillac made motoring history again with the introduction of the Delco ignition, lighting and self-starting system.
Though not the first self- starter, this system, the.joint creation of Cad iliac and Charles F. Kettering's Delco Laboratories, is recognised as being the first practical complete electrical system for a car, the forerunner of all those that have since been developed. This achievement won for Cadiliac another Dewar Trophy-the only time in history this great award has been given twice to the same manufacturer.
Charles Kettering was the catalyst in Cadillac's decision to take another step forward, to bypass the six-cylinder engine and adopt the V8. Kettering and his associates built the V8-powered prototype car that convinced Henry Leland that this was the direction he should follow in the future.
Announced in September 1914 as the standard Cadiliac engine for 1915, the 5150cc V8, developing 70 horsepower, came as an unpleasant surprise to the company's competitors and was both a technical and commercial success.
In fact, since 1915 not a single year has passed in which automotive V8 engines were not being produced at Cadillac - war years included. Engines, aero engines to be precise, were involved in the events that led to the Lelands' departure from Cadiliac during World War 1. The Lelands wanted Cadillac to convert to full production of the new Liberty aero engine, but Billy Durant wasn't so eager to bring car production to a full stop.
The V8 vs. The Straight 8
Henry and Wilfred left Cadillac and set up a new company, the Lincoln Motor Company, from which has grown the most important modern competitor to Cadillac. After the Armistice, Cadiliac entered the auto market of the 1920s with a product of unsurpassed reputation but undistinguished appearance: advanced and stylish bodywork was a rarity on all American cars of that period.
The basic Cadillac was then built on a 132-inch wheelbase, weighed about 4200 pounds, and sold for around $3200. With the help of engineers from the GM research laboratories, Cadillac's V8 was given a new, dynamically-balanced, counter-weighted two-plane crankshaft for the 1924 model year. This made the engine much smoother and fought off, as far as Cadiliac was concerned, the attack of the straight-eight design that enjoyed such a vogue in the 1920s and until the 1930s, fitted to various competitors' cars.
In 1925, Lawrence P. Fisher, one of the six famous coach-building Fisher brothers, became president of Cadiliac. Fisher was to have a strong personal impact on Cadillac's future and one of the first steps he took to secure it was to carry out a five million dollar expansion programme that allowed the GM division to produce 47,420 cars in 1927, almost twice its previous record for one year. In 1925, a new 5.6-liter V8 engine was introduced, having side-by-side connecting rods instead of the earlier fork-and-blade construction. It retained an aluminum crankcase, however, with a separate cast-iron cylinder block for each row of four L-head cylinders.
This new V8 was first produced in a small-bore, 5 liter size in 1927 to power the La Salle, introduced then as a smaller companion car to the Cad iliac. The La Salle was especially significant as the car that prompted Lawrence Fisher to hire a young Californian car designer, Harley Earl, and bring him east to give some shape and style to the La Salle and Cadillac. Subsequently, of course, Earl established the profession of automobile styling and became its leading practitioner. Not even his flair could save the La Salle during the tough years of the depression, however. The last one was produced in 1940.
Synchro-Mesh
Other Cadillac changes during the 1920s included the adoption of four-wheel brakes, in 1923, and the pioneering use of chrome plating over nickel trim surfaces, to prevent tarnishing, in 1928. Also in 1928, Cadiliac became the first car maker in the world to offer a synchronized-shifting transmission, called "
Synchro-Mesh" - a term that has since become part of the English language. Vacuum-boosted brakes were provided on the larger cars in 1932, and the change-over to hydraulic brakes was made in 1937. Many of these changes were the work of Ernest Seaholm, Cadillac's brilliant chief engineer from 1923 to 1943.
The World's First V16 Production Car
In January 1930, the world learned of the finest achievement of Seaholm and Cadiliac - the model 452, the world's first V16 production car. If there had ever been any doubt about Cadillac's role as the premier luxury car of the United States, the fabulous V16 erased it.
Hydraulically-silenced overhead valves were used in the 45-degree, 7.4-liter engine that developed 165 bhp at 3400 rpm and was carried in a special chassis on a 148-inch wheelbase. All coachwork was by Fleetwood, which had become an exclusive supplier to Cadillac in 1926, and prices ranged from $5350 to $9500. In August 1930, Cadiliac introduced a V12 model based on the architecture of the V16, but designed to use the chassis and bodywork of the V8 cars.
These two beautiful engines were part of the Cadillac line until 1937. After that the V12 was dropped and the over- head-valve sixteen, of which 3863 had been built, was replaced by a radical new Seaholm V16 with half the number of parts. It was an L-head design with the cylinder banks at the unusually wide angle of 135 degrees. Only 511 of them were made between 1938 and 1940; since then, Cadillac has remained faithful to the V8.
1941 - A Year Of Revolution For Cadillac
1941 was a year of revolution for Cadillac. The foundation was laid then for the fantastic success the marque has since enjoyed. Planning for it began in 1934, when the shrewd German-born Nicholas Dreystadt was named as Cadiliac's general manager. Under him a new V8 engine was introduced in 1936, a less costly power unit made entirely of cast iron. By 1941, it was producing a very respectable 150 horsepower from 5.7 liters, and it was used in all Cadillacs. Available as an option with it, in that year, was the Hydra-Matic transmission, the first fully-automatic drive offered in Cadiliac's field.
Abandoning The La Salle, And Introducing The True Cadillac Series 61
For 1941, Dreystadt cut back the number of wheel-bases offered from five to three. By abandoning the La Salle, he was able to offer a true Cadillac, the Series 61, at an attractively low price: $1445. That year the Cadillac also appeared with a bold new grille design, the work of Harley Earl and the brilliant young head of the Cadillac Studio, William Mitchell. It was a horizontal, rectilinear egg-crate design that is the un-mistakable progenitor of all the Cadiliac grille designs since. So successfully were these cars received by the public, that 66,130 models were sold, making 1941 the best year yet.
Introducing The Tail Fin, An Inspiration From The Lockheed Lightning Interceptor
A more rounded sports body was introduced in 1942, re-introduced in 1946 and changed only slightly in 1947. In the next two years, however, Cadiliac successively stunned the auto industry with two quite different innovations. The first one, which appeared in 1948, was the tail fin. Those first fins were the direct result of a visit by Earl and his stylists to an airport near Detroit to see the then-new Lockheed Lightning Interceptor, the twin-boom, twin-tail P38. Those first Cadillac fins may look miniscule today, but they sent shock waves through the whole motor world at that time.
Cadillac's second startling step forward was under the bonnet: a high-compression overhead-valve V8 engine, introduced in 1949. It traced its beginnings back to 1937, when the engineers started experimenting with overhead valves and five main bearings (instead of three) as aids to the attainment of better efficiency from higher compression. The fruits of their labours were evident in the lighter weight and higher power of the 1949 engine, most powerful of the American cars of the time, with 160 horsepower from 5430 cc. This widely copied engine established for Cadiliac a new and unusual image, that of a performance car.
Fordillacs
'Fordillacs' became popular-Fords fitted with the powerful Cadiliac engines. Edward Cole Was then chief engineer of Cadiliac and he encouraged those who wanted to use these luxury cars in sporty ways. At
Le Mans in 1950, a Cadillac-engined Allard was placed third, a basically standard Series 62 coupe was tenth and a special-bodied Series 62 finished eleventh. After 1951, however, the new hemispherical-head Chrysler V8 moved ahead of Cadiliac's more durable design in power and sparked the beginning of the famous 'horsepower race'. Cadiliac followed Chrysler in offering power steering, making it standard equipment in 1954.
The 1955 Eldorado Brougham
The next year the premium Eldorado series was introduced, with 270 horsepower under the bonnet and with ventilated, forged-aluminum wheels. Among the experimental cars shown by Cadiliac in the mid 1950s, the heyday of the dream cars, was the Eldorado Brougham of 1955, a very handsome smaller car. It went into limited production at the end of 1956 with such, then-revolutionary, features as quadruple head- lights and self-levelling air suspension. It was a clean-lined four-door car with a brushed-stainless-steel roof panel.
A different kind of Eldorado Brougham was built in 1959 and 1960 - a larger car with crisp lines, built in Turin by Pininfarina to GM designs, at the rate of only 75 a year. The 1959 and 1960 standard Cadillacs marked the peak, both literally and figuratively, of the tail-fin craze. After that, the stylists, now led by Bill Mitchell, started trimming the fins back until they were blended into the wing again in the outstandingly crisp and formal 1965 model. Front-end cornering lights, coming on automatically when the turn signals were operated, were first offered by Cadillac. So, in 1964, was fully automatic Comfort Control, which either heated or cooled the interior as needed to reach the temperature the occupants wanted.
1964 was the year that Cadillac produced its three-millionth car, at a time when the company said it was offering so many options that it could keep its production lines going for three years without having to build two identical cars. The 1967 model year was the first in Cadillac history in which more than 200,000 cars were built. Contributing a little more than ten per cent of that total was a brand-new car with a familiar name, the Eldorado.
This was a new kind of Eldorado, a close-coupled coupe with a long bonnet, that imitated the extravagance of the great V16, and front-wheel drive-the first and only Cadillac with this feature. It used the drive train developed for the
1966 Oldsmobile Toronado and was clothed in a razor-edged body that sold very well to buyers who were mainly aware that it was a 'sporty' Cadillac and who probably had no idea which the Eldorado only, its stroke length was increased to bring the capacity to 8.2 liters, a round 500 cubic inches.
Power and torque rose to 400 bhp (gross) and 550 Ib ft. The ratings are less impressive now, but the strong performance was still on tap. Autocar wrote of a 1970 Cadillac, 'The car gets under way with a majestic surging ease'. George R. Elges, a former manufacturing man, became general manager of Cadillac in 1969 and led the division to new production peaks. 1972 was the first quarter-million-car model year, with a total of 267,787 Cadillacs produced. The Eldorado has since passed through one very successful restyling, so much so that a 1972 model was chosen by US President Richard Nixon as a suitable gift to Soviet leader Leonid Brezhnev during his visit to Russia.
In 1971, an Eldorado convertible was added, the only such model then offered by any of the American luxury makes. Engineering improvements in the normal Cadillacs were not overlooked. For example, variable-ratio power steering was pioneered by Cadiliac, in the US, in 1966. For the 1968 model year, an extensively re-designed engine of 7.75 liters was introduced, simplified for easier service with ten per cent fewer parts and 25 per cent fewer gasketed joints. Its gross output was 375 bhp, with a peak torque of 525lb.ft.
In 1970, for chief engineer, Robert Templin, was recruited to work on GM's Wankel rotary-engine project. Elges and his associates studied the increasing popularity of Mercedes-Benz cars in the United States and formulated the policies which led to the trend of smaller, more economical models. The prime Cadillac example of the trend was the compact Seville, introduced in 1975.
While complying with the ever-increasing mountains of legislation which governed all aspects of the American motor car, and with the pressures which were costing many cars their individuality, Cadillacs managed to maintain their own high standards and their own unmistakable identity - true to the traditions of the man who started it all, Henry Leland.
The Cadillac Cimarron
In an attempt to appeal to younger buyers, Cadillac launched the compact Cimarron in 1982. The Cimarron shared the J platform with the Chevrolet Cavalier, Buick Skyhawk, Oldsmobile Firenza, Pontiac J2000,
Holden Camira, Isuzu Aska and Opel Ascona, and was expected by GM leadership to rival the BMW 3-series in sales performance.
As the Cimarron was rushed to production about three years ahead of schedule, only the notably low powered GM 122 engine four-cylinder engine was available initially (a V6 arrived in 1985) and, at first, very minimal styling differences were made to distinguish it from the considerably cheaper Chevrolet version. Buyers generally dismissed the Cimarron as a "warmed-over Cavalier" with leather seats. Styling became more in tune with other Cadillacs in its later years, but sales did not significantly improve after its initial rejection and it was discontinued in 1988.
V8-6-4 and HT4100
Another nadir during the early 1980s was the variable displacement engine, branded the L62 V8-6-4 engine. Introduced in 1981 this 6 L (368 cu in) engine selectively activated and deactivated cylinders according to power demand. Though the mechanical parts of the engine were sturdy and rugged, the electonics proved unreliable. Cars equipped with the V8-6-4 often ended up returning to dealers and having the electronics disabled to make it run like a conventional V8 engine. The V8-6-4 was dropped from all models, except the Fleetwood limousine, the next year in favor of a family of smaller aluminum V8 engines rushed into production. The HT-4100 4.1 L (250 cu in) engine was used widely in Cadillacs from 1982 through 1987.
Many HT4100s failed before 60,000 miles (97,000 km) and many of the 1,000,000 HT4100s installed in 1982-1987 Cadillacs were replaced by the factory under warranty, although motors with proper maintenance did often run for a great many miles with few to no issues. The HT4100s problems were far less serious and prevalent than those in the one-year-only V8-6-4, but still cost Cadillac the loyalty of many customers.
Cadillac introduced the 4.5-liter aluminum V8 in 1988 which proved to be a very reliable motor, these motors often see well over 250,000 miles (400,000 km). This power plant was bumped up to 4.9 liters in 1991 and ran until 1993. The famous Northstar V8 was then phased in and would power the nucleus of the Cadillac line from the 1993 model year through the next decade.
The Cadillac Allanté
Cadillac tried to rebuild its image in 1987, aware that imported European and Japanese performance models were on a rise, and with Honda launching its American luxury division, Acura. Some new design approaches were tried: the Seville was downsized to BMW 5 series proportions and had rounded wheel arches with only a hint of chrome. During this period, the greatest challenge to the import sports cars was the Cadillac Allanté, a convertible designed by Pininfarina of Italy, and built on what was touted as the world's longest production line - with the car's bodies fabricated in Italy and flown by Boeing 747 to the United States to meet their transmission and engine.
In the initial two years of production, Cadillac offered no options for the Allanté except for the interior and body color. Like the Cimarron of a few years earlier, the Allanté was introduced with an engine which was below the expectations of its target market. The 170 horsepower (130 kW) HT-4100 engine was insufficient against more powerful competition.
This introductory platform turned off many potential customers, who considered the vehicle to be underpowered for its $55,000 price tag, causing them to conclude that Cadillac was not genuinely committed to building a performance car. In 1989 the powertrain was improved with the 4.5 L engine producing 200 horsepower (150 kW). Finally, in 1993 the powertrain was again upgraded to respectable performance with the 4.6 L Northstar V8 producing 290 horsepower (220 kW). This turned out to be the final year of production, as Allanté sales never reached the volume which Cadillac hoped for.
Downsizing and the Brougham
The Cimarron and Seville models marked a beginning of "smaller" cars for the Cadillac line. Throughout the 1980s, American auto makers downsized most of their models and Cadillac was no exception. For the 1985 model year, the DeVille was dramatically downsized and utilized front wheel drive. The Eldorado and Seville were both redesigned and downsized for 1986. By the late '80s, the Fleetwood Brougham was the only Cadillac model that retained the style and size of the "big" DeVilles and Fleetwoods of the '70s.
The "Fleetwood" name was removed from the Brougham in 1987 and the front-wheel drive "Fleetwood" models were technically DeVilles with a special interior and trim option. The Brougham was redesigned in 1993 and renamed the Fleetwood, with an optional Brougham package, towing capacity is up to 7,000 pounds (3,200 kg) with the L05 V8. In 1994 Cadillac replaced the L05 engine with the new more powerful LT1 engine. The Fleetwood was discontinued after the 1996 model year. Following the demise of the Fleetwood, the Lincoln Town Car was left as the sole traditional full-sized luxury car remaining in the U.S. market.
Competition with Lincoln
After GM phased out the D platform in 1996, Cadillac was left with a completely front-wheel drive lineup except for the European-based Catera, introduced for 1997. The GMC Yukon Denali-based Escalade, Cadillac's first sport utility vehicle, was introduced in 1998 for the 1999 model year, and featured standard all-wheel drive. It was quickly created to capitalize on the instant market success of the Lincoln Navigator launched as a 1998 model and seemingly destined to propel the Lincoln brand's sales total for the 1998 calendar year well ahead of Cadillac's.
By November 1998, Lincoln's year-to-date lead was a comfortable 6,783 vehicles, but Cadillac's December sales were reported as 23,861 vehicles, more than 10,000 ahead of its November sales. A prominent proportion of this increase was a rise in Escalade sales from 960 in November to 3,642 in December. The result was an overall lead for the Cadillac brand by a slim 222 vehicles. Subsequent audits of sales records during the first quarter of 1999, prompted by the unusual numbers posted in December plus the fact that Escalade sales had dropped to a mere 225 vehicles in January 1999, resulted in the discovery of an "error" of 4,773 units. With this corrected, it meant that Lincoln had in fact passed Cadillac in total sales for the 1998 calendar year (187,121 Lincolns sold vs. 182,570 for Cadillac).
In the first week of May 1999, a public retraction and apology was issued by GM spokesman Jim Farmer, admitting that "a combination of internal control breakdowns and overzealousness on the part of our team members" was the cause of the overstated figures, and adding that those responsible had been disciplined. However neither brand would have any reason to celebrate any sales success in the US luxury market as their prior number one and number two positions had been overtaken by Japanese and German brands.
